Describe the Structure of the Sarcomere
Describe the structure of the sarcomere and explain how it enables muscle contraction according to the sliding. Skeletal muscle is the type of muscle that is used in voluntary movement and the heart muscle is the muscle that is part of the heart.

Sarcomere Definition Structure Function And Quiz Biology Dictionary
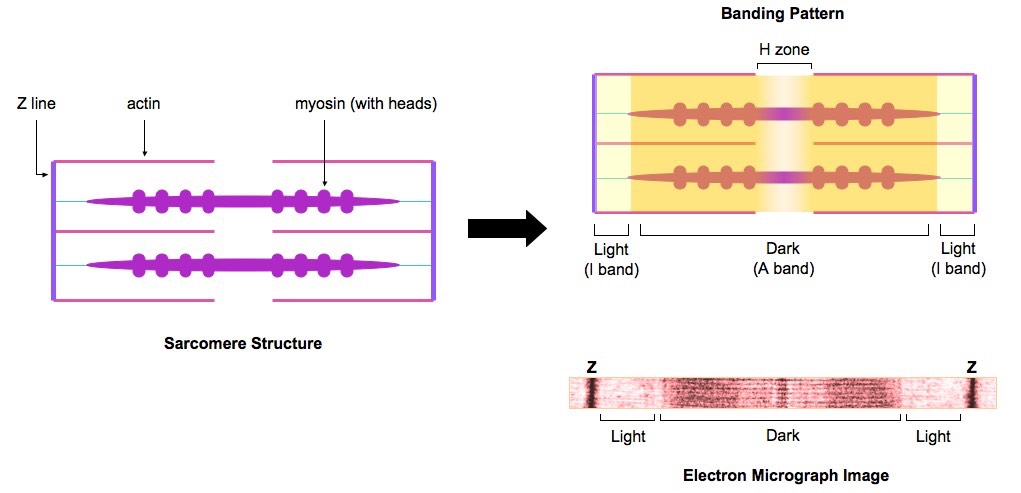
The myofibrils consists of repeating sections of sarcomeres which appear as alternating dark and light bands.

. A sarcomere has primary and secondary myofilaments. B Explain the sliding filament model of contraction using appropriately labeled diagrams of a relaxed and a contracted sarcomere. The operating unit of a striated muscle is a sarcomere.
The sarcomere is termed as a basic unit of striated muscle tissue and skeletal muscles are made of tubular muscle cells myocytes and myofibrils of muscle fibers and are developed by the process called myogenesis. Skeletal muscles is made up of tubular muscle cells. A sarcomere is the portion of a myofibril that lies between two successive Z disks.
Sarcomere structure When viewed under a microscope muscle fibers of varied lengths are organized in a stacked pattern. The myofibril strands thereby actin and myosin form bundles of filament arranged parallel to one another. The myofilaments are within the sarcomere.
Describe the structure of sarcomere. Each muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Each sarcomere divides into different lines bands and zone.
It forms the repeating unit between two Z lines. As illustrated in Figure 2-5 each sarcomere contains two types of myofilaments. Describe the structure of the sarcomere and explain how it enables muscle contraction according to the sliding-filament model.
Muscle fibres of varying lengths are arranged in a layered pattern as viewed under a microscope. The sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle. They are highly organised within skeletal and cardiac muscle which give a stripedstriated appearance to the muscle.
The muscle form that starts all of our voluntary activity is skeletal muscle. The central region of the A zone H zone contains only thick filaments myosin and became short during contraction. Sarcomere a molecular structure in myofibrils that allows cardiac myocytes to contract and generate force.
It is made of thick and thin filaments. Describe the structure of sarcomere. The structure of the sarcomere is organized into bands of interdigitating thick filaments and thin filaments.
The portion of the myofibril between two successive z lines is called as sarcomere. Structure of sarcomere- A skeletal muscle fiber comprises several myofibrils which are rod shaped and these myofibrils runs parallel to the length of the muscle. The boundary of the sarcomere are the Z lines.
Each sarcomere is composed of two main protein filamentsactin and myosinwhich are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction. A sarcomere it is the fundamental functional unit of striated muscle that is of skeletal and cardiac muscle. A sarcomere is defined as the region of a myofibril contained between two cytoskeletal structures called Z-discs also called Z-lines and the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement of the thick and thin myofilaments within each sarcomere Figure 1022.
A sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber. The myofibrils consists of repeating sections of. Thick filaments composed primarily of the contractile protein myosin and thin filaments composed primarily of the contractile protein actin.
A sarcomere consists of thin and thick filaments arranged so they can slide over each other. I and A bands M and Z lines and the H zone. This implies that our skeletal muscle consists of the most fundamental unit.
Thick filaments attach to the middle of the sarcomere or M line and. The thick and thin filaments. Structure and Parts Functions and Histology.
A sarcomere describes as the distance between two Z discs or Z lines. Sarcomere are the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. When a muscle contracts in our body the distance reduces between the Z discs.
Sarcomere is a structural and functional unit of a muscle fiber. These myofibrils again posses contractile elements and functional unit of skeletal muscle called sarcomere. To say that the sarcomere is the functional unit means that all the components.
Skeletal muscles is made up of tubular muscle cells. A sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber. The process is energized by ATP.
The dark band or Anisotropic band A band is made of myosin and the light band on Isotropic band I- band is made of actin filaments. The most popular model that describes muscular contraction is called the sliding filament theory. The theory proposes that the thin filaments slide toward the center of the sarcomere through the ratchet like action of the myosin heads.
In this theory active force is generated. Problem 23 Hard Difficulty a Describe the structure of a sarcomere and indicate the relationship of the sarcomere to myofilaments. The sarcomere is the basic repeating unit of muscle formed by two transverse filament systems.
Each muscle fibers contain numerous tubular myofibrils. Myofibrils appear on alternate light and dark bands and are composed of repeated sections of sarcomeres. A sarcomere is the region of a myofibril between two successive Z-lines and is the smallest contractile unit of a muscle cell.
Each sarcomere is composed of two main protein filaments- actin and myosin which are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction. Sarcomere consists of an A band with half I band at each end of the A band. A sarcomere is the functional unit contractile unit of a muscle fiber.
It is the functional unit of muscle contraction. Thin filaments also contain the regulatory proteins troponin and tropomyosin. A sarcomere consists of a dark band in the centre and light bands on either side.
While actin and myosin are the main contractile elements of the sarcomere other proteins act as scaffolds control ultrastructure composition regulate muscle contraction and transmit tension between sarcomeres and hence to the whole myofibril. It forms the repeating unit between two Z lines. Sarcomere are the basic unit of striated muscle tissue.
Watch location of the sarcomere video Sarcomere Components. Thick filaments are organized bundles of myosin while thin filaments are made of actin along with the two other regulatory proteins troponin and tropomyosin. Number of sarcomeres together form myofibril and contraction of the sarcomere ultimately result sin contraction of the muscle.

No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Sarcomere"
Post a Comment